Sunlight is white, that is, it includes all the colors of the spectrum. It would seem that the sky should also be white, but it is blue.
Surely your child knows the phrase “Every Hunter Wants to Know Where the Pheasant Is Sitting”, which helps to remember the colors of the rainbow. And the rainbow - the best way understand how light breaks into waves of different frequencies. The longest wavelength is in red, the shortest is in violet and blue.
The air, which contains gas molecules, microcrystals of ice and water droplets, scatters light with a short wavelength stronger, so the blue and purple colors in the sky are eight times more than red. This effect is called Rayleigh scattering.
Draw an analogy with balls rolling down a corrugated board. The larger the ball, the less likely it is to stray or stick.
Explain why the sky can not be other colors
Why is the sky not purple?
It is logical to assume that the sky should be purple, because this color has the shortest wave. But here come the features of the sunlight and the structure of the human eye. The spectrum of sunlight is uneven, shades of purple in it are less than other colors. And the human eye is not visible part of the spectrum, which further reduces the percentage of shades of purple in the sky.
Why is the sky not green?
amopintar.comA child may ask: "Since scattering increases with decreasing wavelength, why is the sky not green?" Scattered in the atmosphere is not only blue rays. Their wave is the shortest, so they are more noticeable and brightest of all. But if the human eye was arranged differently, the sky would seem green to us. After all, the wavelength of this color is slightly longer than that of blue.
Light is not like paint. If you mix green, blue and purple paint, you get a dark color. With light, the opposite is true: the more colors that blend, the brighter the result will be.
Tell us about the sunset
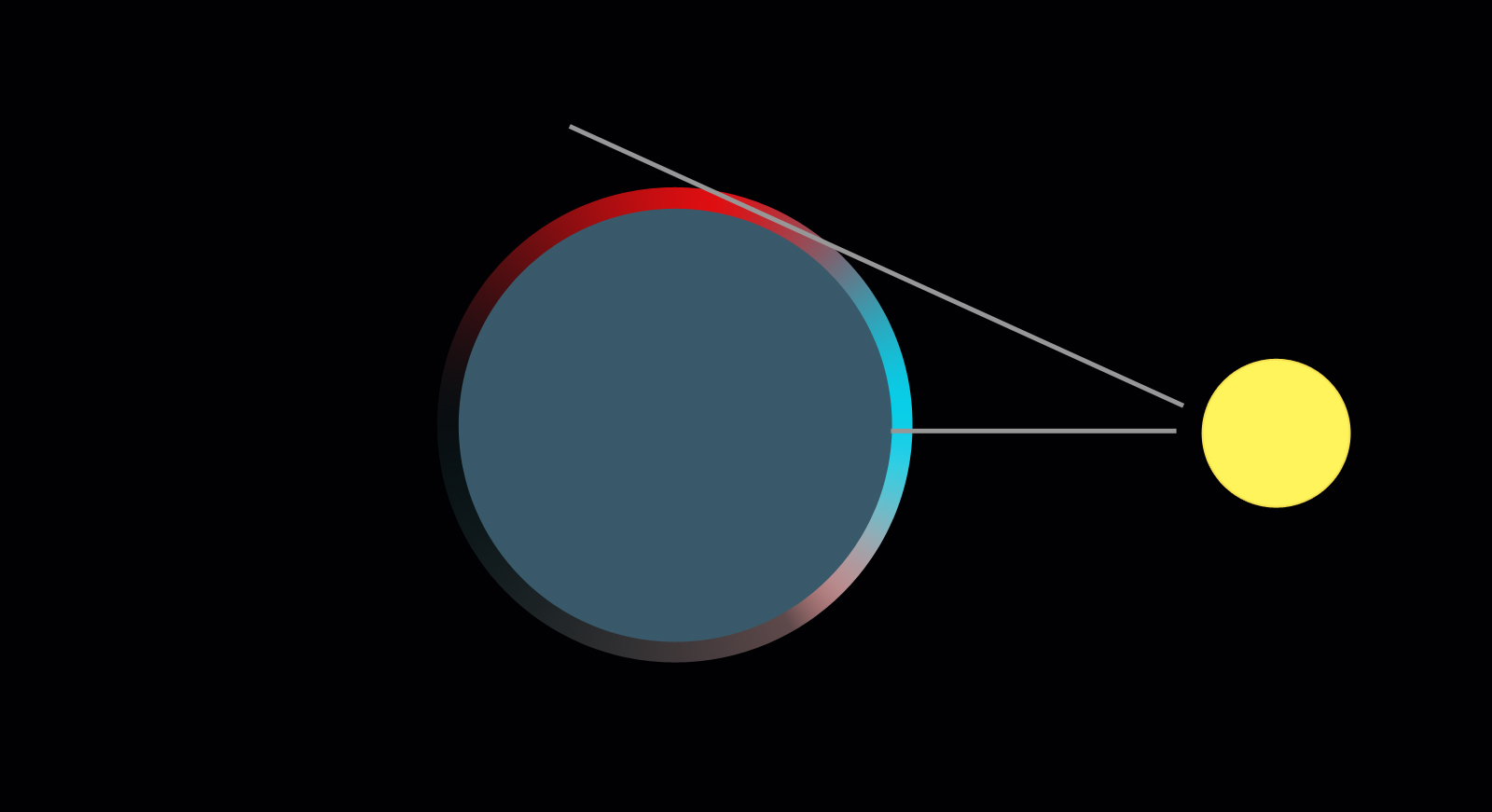
We see blue skywhen the sun shines from above. When it approaches the horizon, and the angle of incidence of the sun's rays decreases, the rays go tangentially, going a much longer way. Because of this, the waves of the blue-blue spectrum are absorbed in the atmosphere and do not reach the Earth. In the atmosphere, red and yellow are dispersed. Therefore, at sunset the sky turns red.
The sun not only gives us light and heat, but also paints everything around us in the rainbow colors of the spectrum. The ray of white light is actually multicolored; we know this by its reflection in a drop of rain that has become a rainbow. Then why for the sky did the sun choose precisely blue, and not green, for example? Although it is very difficult to imagine a green sky.
The earth is surrounded by a layer of air that we breathe. It contains oxygen, ozone and carbon dioxide. This layer is called the atmosphere. The thickness of the atmospheric layer is about 500 kilometers. It contains the air we breathe.

Air consists of molecules in which light cannot reflect. He scatters on them. Electrons in a molecule come under the influence of sunlight falling on them and begin to radiate it. And the light itself is scattered. And we see this scattered light from the Earth.
Gases in the air divide the light into the known colors of the spectrum. We know them well we know - red, orange, yellow, green, blue, blue, purple. But we, most often, see blue or blue. Why the sky is blue?

Here comes into force the law of dispersion, discovered by Rayleigh, according to which light with a shorter wavelength is scattered faster than light of waves with a greater length. The blue, blue and purple colors of the spectrum have a smaller wavelength. Therefore, it is their diffused light that we see in the sky.

Some colors of the spectrum with a longer wavelength, such as red and orange, are almost not dispersed. At sunset, the layer of the atmosphere increases many times, the spectrum is more difficult to pass through, and since the blue and blue colors are scattered, they remain less and less in the palette of celestial colors in the evening, one paint remains intact - red. Here we see it at sunset in the sky. And the sun itself appears to us then red. Of course, in another part of the planet the sky at this moment is blue, the short rays of the spectrum are scattered there.
By morning, the sun returns to us if it does not have to make its way through the thick veil of clouds and clouds. Then we see the sky in the clouds. And this is another story.
1. Why is the sky blue and not green? Answer for dummies
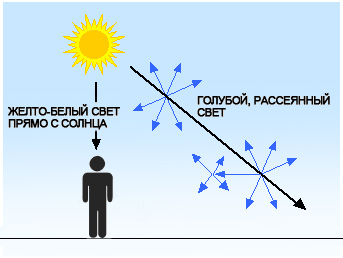
Light from the sun or a lamp looks white, but in fact white is a mixture of all 7 existing colors: red, orange, yellow, green, blue, blue and violet (Fig. 1). The sky (atmosphere) is filled with air. Air is a mixture of tiny gas molecules and small pieces of solid material, such as dust, for example. As sunlight passes through the air, it collides with air particles. When a beam of light hits a gas molecule, it can “bounce off” in another direction (scatter). Some composite colors of white light, such as red and orange, pass from the Sun to our eyes directly, without scattering. But most rays blue "Rebounds" from air particles in all directions. Thus, the whole sky is literally penetrated by blue rays. When you look up, a part of this blue light reaches the eye and you see a blue light everywhere above your head! Here, actually, why the sky is blue!
Naturally, everything is simplified to the maximum, but below is a paragraph where the property of our beloved sky over your head and the reasons that explain why the color of the sky is blue rather than green is more fundamentally described.
2. Why is the sky blue? Answer for advanced
Let's take a closer look at the nature of light and color. Color, as everyone knows, is a property of light that our eyes and brain can perceive and define. Light from the sun - a large number of white rays, which consist of all 7 colors of the rainbow. Light has the property of dispersion (Fig. 1). Everything is illuminated by the Sun, but some objects reflect the rays of only one color, for example, blue, and other objects - only the rays of yellow and so on. Thus a person determines the colors. So, the Sun shines on Earth with its white rays, but it is enveloped in the atmosphere (thick air), and when this white (consisting of all colors) beam passes through the atmosphere, it is the air that diffuses (spreads) all 7 color rays of the white sunbeam, but with greater force, it is his blue-blue rays (in other words, the atmosphere literally begins to glow in blue). Other colors directly come from the Sun to our eyes (Figure 2).
Why is it that blue color is most susceptible to dispersion in the atmosphere? This is a natural phenomenon, and is described by the physical Rayleigh law. If it is easier to explain, then there is a formula, which was derived by Rayleigh in 1871, and which determines how the scattering of light (beam) depends on the color of this beam (that is, on such a property of the beam as its wavelength). And it just so happened that the sky-blue color has the shortest wavelength and, accordingly, the largest dispersion.
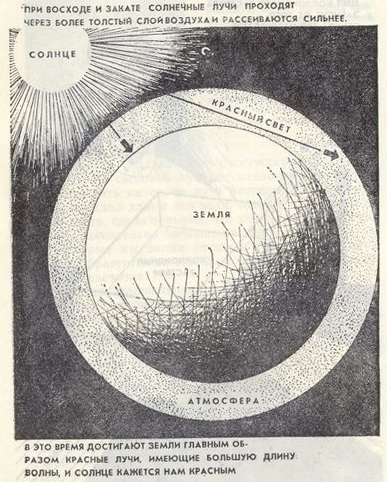
Why is the sky red at sunrise and sunset? At sunset or sunrise, the sun is low above the horizon, because of which the sun's rays are obliquely falling
are on Earth. The length of the beam, naturally, increases many times (Fig. 3), and therefore at such a huge distance almost the entire shortwave (blue-blue) part of the spectrum is scattered in the atmosphere and does not reach the Earth's surface. Only long waves, yellow-red, reach us. This is precisely the color that the sky acquires at sunset. That is why the sky except blue and blue is also yellow and red!
And now for a complete understanding of the foregoing, a few words about what the atmosphere is.
What is the atmosphere (heavenly vault)?
The atmosphere is a mixture of gas molecules and other materials surrounding the Earth. Basically the atmosphere consists of nitrogen (78%) and oxygen (21%) gases. Gases and water (in the form of vapor, droplets and ice crystals) are the most common components of the atmosphere. There are also a small amount of other gases, as well as many small solid particles, such as dust, soot, ash, salt from the oceans and so on. The composition of the atmosphere varies depending on the geographical location, the weather and much more. Somewhere there may be more water in the air after a shower or near the ocean, somewhere volcanoes spew large amounts of dust particles high into the atmosphere.
The atmosphere is more dense in its lower part, near the Earth. It is gradually thinning with height. There is no sharp gap between atmosphere and space. That is why we see the play of blue and blue in the sky, precisely because the atmosphere in the sky is different everywhere, has a different structure and properties.
