The first half year of life of a newborn baby mother's milk is the most complete food. In order for this period to be comfortable for the mother, and for the baby only to bring benefit, every inexperienced mother should know the main and most important rules of breastfeeding.
Putting the baby to the chest. Important points:
Features of modern breastfeeding
- One of the principles is free and unlimited feeding at the first wish of the infant. Unlike the old methods, this method has a positive effect on the child's psycho-emotional state and. It is advisable to give the breast in any restless state of the baby, without waiting for him crying. If a baby in the first months requires 10-16 feedings - this is normal!
- Up to half a year, the infant needs night feedings, as they bring the greatest benefit to the child, and a steady lactation is formed in the mother.
- The duration of sucking depends only on the child. The last milk in the breast is the most fat and healthy, therefore it is recommended to give the baby to suck out one mammary gland until the very end. The second should be offered only in the next feeding. An exception can be only in the case of a lack of breast milk in one breast for complete saturation.
- A baby up to six months can do only breast milk without the introduction of additional power. ()
- The best option for the full development of the child, strengthening the immune system and protection against viruses is breastfeeding up to one and a half to two years.
When breastfeeding is not necessary:
There are several studies on the effect of pasteurization on the immunological and nutritional components of human milk. Therefore, pasteurized milk is not only intended to be fed, like some thoughts, but also to protect the children who receive it. The definition of fat contained in milk is important because it is the main source of energy for newborns. The use of exclusive breast milk presents some limitations due to the mother’s ability to promote adequate supply, the gastric capacity of the newborn and the undesirable effects of water overload.
- Often wash mammary glands, as frequent washing removes the protective fatty layer from the nipples. The absence of a protective film leads to painful cracks in the nipples and areola. It is enough to take a shower once or twice a day.
- Giving a child water - excess water can reduce appetite and increase flatulence in the baby's digestive system. A teaspoon of water per day can only be given if the child’s constipation is constipation from mom's fat milk.
- Before half a year, use pacifiers and water from a bottle. If the baby does not have enough milk, supplementing should be given with a spoon or a pipette. An infant may confuse breastfeeding with a nipple (it is harder to suck milk from a breast than from a bottle), and improper sucking can lead to nipple cracks. In addition, the baby can completely abandon breast milk.
- After each feeding, rescue milk residues. The exception is stagnation in the chest, engorgement or forced separation of the mother from the baby.
- Weigh the baby often. It is enough to control the weight once in one or two weeks. Frequent weighing can unnerve the mother and induce the introduction of unnecessary supplements.
- To feed the baby with sweet tea. Sweet can harm future teeth, and tea can contribute to iron deficiency anemia.
Video №1
Supplement retains the basic advantages of human milk and can be made according to different methods. One possibility is to use the most dehydrated human milk or its parts, but this is not common practice because of the difficulties in obtaining large volumes of milk for such preparations. Many of the available reinforcing agents are derived from cow's milk or protein hydrolysates, so the profile of amino acids in these cases differs from that obtained with human milk, although it provides a large proportion of proteins and minerals.
Video №2
It has been established that early attachment of the baby to the breast after birth contributes to the more rapid formation of lactation. Therefore, now the mother begins to breastfeed for the first time 2 hours after birth.
However, breast milk, when present, should be prioritized, and its strengthening is a desirable practice and leads to good results. Stimulating milk collection from mothers of premature babies is presented as a resource that allows you to maintain lactation and adequate breastfeeding of these babies. It is necessary that the collected milk represents the minimum bacterial contamination, so that it preserves its microbiological quality, providing characteristics that are responsible for the biological value of milk and the safety of the newborn.
Before each feeding, the mother should wash her hands thoroughly with soap and wash the nipple with a cotton swab moistened with boiled water or 2% boric acid solution (one teaspoon of boric acid per cup of boiled water). Every morning, before breastfeeding, both breasts should be washed with soap and water. When feeding, a kerchief should be worn on the head, and a gauze mask on the face during the first month of life of the child. The first portions of milk from the breast (one teaspoon) are better to decant and pour, as there may be microbes.
Storage should be carried out in such a way as to preserve its nutrients while maintaining its quality. Although processing can lead to a reduction in immunobiological indicators, it is the best method for preparing milk that needs to be stored for a long time, in addition to ensuring its safety when breastfeeding. Let's start with a few small concepts.
However, studies have shown that a child from one week to one month consumes an average of 150 ml of milk per kilogram per day. Between a month and six months baby drinks an average of 800 ml of milk per day. This amount does not change or almost during these five months. However, the result will necessarily be wrong, as the baby does not necessarily drink the same amount with each feeding.
- It's almost impossible to recognize a drunken baby in the chest.
- Therefore, a child of 3 kg will drink an average of 450 ml per day.
- The amount received during the first month.
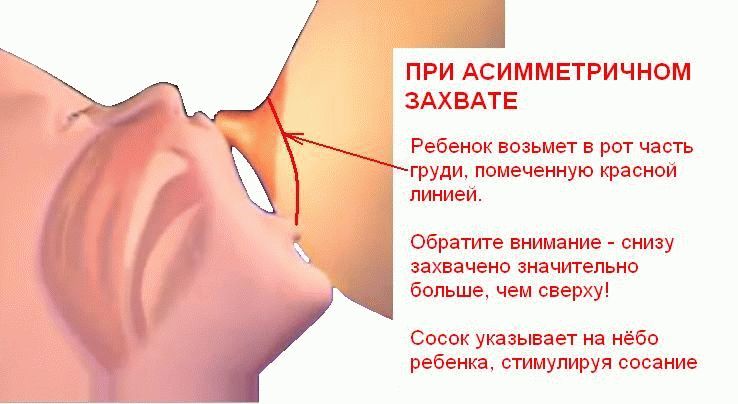
The first day after birth, the mother should be fed the baby lying on its side, while putting the baby so that his mouth is against the nipple. While supporting her breast with her hand, the mother puts the nipple into his mouth, while with her thumb she presses the breast down slightly so that she does not close the baby’s nose and prevent it from breathing. It is necessary to ensure that the child captures not only the nipple, but also the islet circle. He knows how to suck from the very birth, but sometimes the first feeding is still unsuccessful: the baby doesn’t grab the nipple, loses it and falls asleep. Such children learn to suck only after a few days. In these cases, you need to express a few drops of milk to the baby, pressing down on the breast, and he immediately begins to suck. If the baby is weak, you need to express milk from the breast for feeding and give him 3-5 teaspoons each time.
However, most children take a different rhythm with the person who holds them. At first they do not necessarily take a large number of new people, it takes time until they find their new rhythm. So the easiest to try! If your child needs to take powdered milk, do not worry, it will be restored to 30 ml per 30 ml. If you leave breast milk first, pay small amounts. A bottle, started, but not finished, is often thrown into bed, it would be a pity to spoil the heavily loaded breast milk!
Gradually, you will discuss with the person who cares about your child, and adapt the amount to be left. If a bottle is given to a baby who is usually breastfed, he often tends to drink it too quickly. In fact, it must be swallowed with every movement of suction, while swallowing every two or three sucks. Therefore, it is a bit of a “trap”. Now a child who drinks too fast will drink too much, because the feeling of fullness does not have time to come.
In the first 2-3 days, the baby gets a small amount of milk (colostrum) from the mother’s breast, from the 5-6th day of milk it becomes more, and by this time the baby begins to suck more vigorously. On average, the baby’s sucking lasts 15–20 minutes, and some children suck out the required amount of milk in 8–10 minutes.
On the second day after birth, the baby should be breastfed while sitting, leaning back against the back of the chair. One leg, according to the breast that is fed, should be placed on a small stool. In one feeding it is necessary to give the child only one breast, in the next feeding - the other. With this alternation, the mammary glands are almost entirely exempt from milk, which contributes to the development of it in sufficient quantity.
Benefits of Breastfeeding
The nursery can therefore tell you that you do not supply enough milk! Then you can explain the problem by asking them a lot of breaks for your child when he drinks a bottle. To enlighten you, here are the pros and cons of each option.
Rich in essential nutrients
Breast milk is a living substance that constantly reacts to changes in the child and his environment, contains all the nutrients necessary for the development of the newborn, and is rich in antibodies that help prevent and control intestinal infections, respiratory and auditory.With an insufficient amount of milk, you can attach the child during one feeding and to the second breast, but always after the first emptying. In this case, the second breast is usually not completely emptied and the remaining milk is not decanted. Then at the next feeding the second breast should be given at the beginning of the feeding. It is necessary that the child sucks the breast completely, the rest of the milk after feeding must be decanted.
How to feed a newborn baby from a bottle?
Breastfeeding also reduces the risk of future allergies in the infant, and breast milk is easily absorbed, which makes the baby less prone to diarrhea and constipation and protects it, moreover, against the risks of diabetes, cancer and leukemia. About 3-5 days after birth, your breasts produce colostrum, yellow and creamy fluid rich in antibodies. From the 6th to the 14th day, your breasts release transitional milk, and then produce mature milk after the 14th day. Milk also changes during breastfeeding: at first it is clear, slightly bluish and rich in water to moisten the baby, then it becomes thick and creamy to satisfy it, but the composition changes depending on whether your baby is premature or term.
It is important to know that the first portions of milk contain less fat and mineral salts, and the last - more. Milk should be decanted with clean hands in boiled dishes and stored in the cold. Before feeding, it should be heated in a bottle, dipped in warm water, and feed the baby from a spoon.
When breastfeeding, the mother must ensure that the child does not swallow air during the sucking process, as this leads to regurgitation. To avoid swallowing air, it is recommended to help the child with feeding - to support the breast, so that it captures not only the nipple, but also the areola. After feeding, hold the baby in an upright position for 1-2 minutes so that it bursts out air that could be swallowed while sucking. Then you need to wash the breast again with boiled water, dry it with a clean cloth, brush the nipple with petroleum jelly, put a clean, ironed pad between the bra and the breast to avoid irritation and rubbing of the nipple about the underwear. In the intervals between feeding should always support the breast with a free bra.
Natural and accessible to all
Breastfeeding provides a natural and unique experience for the mother, direct and privileged contact with the child, a gesture that is more than a means of feeding, a mother who breastfeeds between the child and the child. also play a role as they play an important role in their role of helping with the mother. Each woman's body is intended for breastfeeding, so 98% of the medications given to the mother are not contraindicated during breastfeeding. Your doctor can tell you about it.
During breastfeeding, the mother should be focused, think only about the child. This helps to increase lactation (other ways, read the article "How to increase lactation"), as well as a positive effect on the body of the infant. No other distracting talk is allowed.
Finally, some foods will not create intolerance or colic in a child, as some claim. When you are breastfeeding, you do not have a bottle for preparation, cleaning and sterilization, and the milk that you produce is available at any time and at the right temperature. All you need is a place to sit comfortably.
How much should a newborn breast feed?
Breastfeeding causes hormones that cause uterine contraction and promote weight loss during pregnancy. Providing breast also helps lose a few pounds and produces a contraceptive effect. However, this method of contraception is only effective for 6 or more feedings per day and is far from being 100% reliable! Studies show that breastfeeding for 12 months for a 30% risk of breast cancer during premenopausal and breastfeeding for at least 2 months would reduce the risk of ovarian cancer by 25%.
In cases of flu, sore throat, cough and runny nose, each mother should put on a gauze mask (3-4 layers) covering her mouth and nose while breastfeeding and caring for her. When coughing and sneezing, you must turn away from the child, and even better - go to another room.
Digestion of milk in the stomach and its transition into the small intestine of a child takes 2.5-3 hours, so it is recommended to take such breaks between feedings. Until the age of one month, the child must be fed 7 times a day, with a night break of 6 hours (at 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24 hours). From one month of age, most children are transferred to a six-meal meal after 3.5 hours (at 6, 9.30, 13, 16.30, 20, 23.30), and from 5 months - five times a day, after 4 hours (at 6, 10, 14, 18, 22 hours), with an 8-hour night break.
Breastfeeding Disadvantages
Breastfeeding requires a lot of accessibility, especially during the first few weeks of feeding your baby according to your needs, and you can gradually adopt a breastfeeding schedule that is more compatible with your daily life. A breast pump will allow you to prepare bottles for breast milk to help you.
Will milk have time to digest, if the child asks the breast often?
During the first few weeks, milk growth may be irregular, both in terms of quantity and on schedule. During this period, avoid as many extra feeding bottles as possible and the breast pump to maximize the success of your breastfeeding. Milk growth will be regularized after 2 or 3 weeks, and breastfeeding will be much easier.
This feeding regime continues until the end of the year. Hours of feeding depending on the home environment may vary. However, these changes, once established, should be observed in the future. It matters both to the child and the mother. Exact adherence to diet quickly produces conditioned reflex for a while in the processes of secretion of digestive juices in the child and the production of milk in the mother. When approaching the time of feeding the child wakes up, he has an appetite.
It is usually difficult to breastfeed, but this situation is not normal. Good accompaniment can avoid this pain due to poor grip or poor posture. Usually in the first few days of breastfeeding, breast cracks that make feeding painful may be caused by too long feedings, or a baby who stretches the nipple or takes all the areolae in the mouth.
Breastfeeding Nutrition
Stasis is the result of poor drainage of the breasts. If heads are limited, duration, frequency, if the head is jumping, an overload may occur. The chest quickly fills up and becomes swollen, heavy and sensitive. Because there may be a lack of elasticity of the skin, insufficient evacuation of the breast or poor breastfeeding of the infant.
Often, mothers have the following question: what to do if the baby sleeps at the set feeding time, wake him up? Or like this: is it possible to feed a child before the scheduled time, if he wakes up and cries? If the baby wakes up feeding time, it should not be awakened. If the child shows a feeling of hunger earlier, you can feed him without fear of the harmful effects of eating disorders.
Quality of dairy products
Some women will experience more such inconvenience than others. Fortunately, now there are cups and cotton protectors to soften the flow of nipples. Some women may not or do not want to breastfeed. Dairy products, which have developed significantly since the very beginning, meet the basic nutritional needs of children. It contains proteins, fats, calcium and iron. Whether it is powdered, concentrated or ready to eat, it also contributes to the normal development of the baby’s brain, eyes and immune system.
It is very important that the baby is provided with the necessary amount of milk. It must be remembered that both underfeeding and overfeeding adversely affect the health and development of the baby. With insufficient nutrition, children grow poorly, their metabolism is disturbed, their digestion is upset.
The required daily amount of milk for a child in the first year of life is not the same. It depends on the age and body weight of the child. At the age of two months, he should receive such amount of milk per day, which would be equal to 1/5 of its mass (if a child was born weighing over 4000 g, then 1/6 of its mass is taken), at the age of 2 to 4 months - 1 / 6, from 4 to 6 months - 1/7, from 6 to 9 months - 1/8 of the mass.
Industrial milk is well digested, albeit a bit slower like breast milk, which gives you a longer respite between two meals. However, bottle feeding sometimes causes overfeeding, and mothers rely more on bottle feeding to determine the frequency and length of breastfeeding, rather than the requirements of their baby.
How much to breastfeed
One of the main benefits of bottle feeding is that you are not the only person who depends on what the baby is feeding on. Your spouse can help you with this task, including nightly drinks! You can also pass the torch to a member of your surroundings to perform other tasks, take a nap or from home. In short, the bottle is synonymous with greater freedom for the mother, especially in several genera!
But in all cases, the total amount of food after four months of a baby’s life should not exceed 1 l. In the first days of life, the baby sucks up to 200 g of milk per day, by the end of the week - about 400-500 g per day (for one feeding - 55-70 g), in the first month of life - 700-750 g (for one feeding - 100 -110 g), by the end of the second month - 800-850 g (110-120 g per one feeding with seven meals), on the 3-4th month - 850-900 g (140-150 g per feeding) with six times nutrition and in the following months 1 l per day (up to 200 g per time with five meals).
In case of diseases, violations of the proper development of the child, the frequency of feeding and the amount of food may decrease or slightly increase as prescribed by a doctor.
What are the signs of adequate and nutritional nutrition of the child?
About the saturation of the child can be judged by his calm behavior in between feedings. He often urinates (15-16 times a day), the number of wet diapers is about 2 times the number of feedings per day. The baby grows and arrives in bulk, it has folds on the hips, arms, its skin is elastic, pink in color.
A sign of malnutrition is the hectic behavior of the child, he cries a lot, does not stand up between feedings. When feeding, the breast is greedy enough, but after a few minutes, throws it out and shouts again. He rarely urinates, diapers remain dry for a long time. The child’s stool becomes rare and scanty, and the tendency to constipation often develops. Its weight does not increase enough - less than 20-25 g per day in the first half of the year and less than 15-20 g in the second. In such cases, it is necessary not to postpone the control weighing of the child before and after feeding during the day, since during different hours of feeding there are significant fluctuations in the amount of milk.
After a night break, the baby sucks more vigorously and sucks more milk than in the next hours of feeding. If it is determined that the mother does not have enough milk, it is necessary to take measures to increase its secretion. In addition, it is immediately necessary to consult a doctor to resolve the issue of supplementing the baby. Prolonged nutritional deficiencies, especially of its protein and fat components, disrupt the development of the child, and have a negative effect on the formation of its immunological reactivity. In children who have suffered fasting in the first months of life, there is a decrease in memory and learning ability.
Between breastfeeding, the baby should receive water for drinking from 50 to 70 g per day in cold weather and up to 100-200 g per day in the roast. It is good to give a decoction of fruit or vegetables instead of a portion of water (unsweetened decoction of rose hips, apple peel, dried or fresh berries).
Should give recommendations for nursing mothers with twins. At first, a weaker baby is applied to the breast, since the first portions of milk are easier to suck off. After breastfeeding, it is necessary to wash the nipple (with a solution of potassium permanganate) and attach the second twin to the same breast in order to empty this breast to the end, and only then give it another breast.
In subsequent feedings they begin to feed that breast in which there is more milk left. It is very important to monitor whether the twins have enough milk, or whether their weight gain is good. To do this, you need to have scales at home and periodically weigh the children before and after feeding during the day, then you can correctly determine if they have enough breast milk. If there is not enough milk, it is advisable to feed the twins with donor breast milk or mixtures that are close to the composition of breast milk.
From one month of age, an infant needs an additional supply of mineral salts and vitamins. To this end, he needs to give raw fruit and vegetable juices. Juices contain vitamins A, C, B, P, they are rich in minerals such as iron, copper, manganese, cobalt, which play a large role in preventing anemia.
It is better to start with apple juice, black currant juice. From two months, recommended carrot, tomato, plum, cherry, raspberry, orange, lemon, cranberry juice. Strawberry and strawberry juices are often the cause of an allergic rash, so they are best given after a year. Grape juice often causes increased fermentation in the intestines, for this reason in the first year of a child’s life it is better to refuse juice.
Juices should be given after meals, as due to their sugar content, consuming them before meals reduces appetite. It is necessary to caution children to juice: start with 1/2 tsp per day, gradually increase the amount of juice, bringing to 1/4 cup by 4 months of age and up to 80 g by the year. Juices should be divided into 2 doses per day. They add sugar or sugar syrup. Very acidic juices diluted with boiled water. Juices are better not to mix. Carrot juice is recommended to be given every other day and not more than 30 g. If the child has a tendency to diarrhea, it is better for him to drink black currant juice, lemon, blueberry, pomegranate juice, and the tendency to constipation is carrot, plum, beet and orange.
From the fourth week of life the child needs vitaminDwhich protects against rickets and contributes to the normal growth of bones and teeth. It should be given as prescribed by the local doctor.
Pretty early in the infant's diet is injected raw grated apple. From one and a half month old, a child can be given a teaspoon of grated apple per day, gradually increasing the dose in 10 days to 30 g (up to two tablespoons). At the same time, minerals, especially iron, are introduced into the body. This is very important, as minerals are involved in the construction of tissues, bone system, are part of body fluids, including gastric juice. Citric acid contained in apples has a positive effect on metabolism, pectic substances tone up the intestines, affect peristalsis, adsorb gases. That's why applesauce Especially useful for children with a tendency to constipation. In addition, apple puree contributes to the early habituation of children to thick foods, which facilitates further their translation to supplemental foods. Very useful canned applesauce, cooked specifically for infants. Banana puree is also useful. After peeling a ripe banana, pound it with a spoon and the mashed potatoes are done. It is very gentle, pleasant to the taste, but it should be given carefully to allergenic children.
If the child has a tendency to constipation, it is recommended mashed prunes (after three months) from 2 to 4 teaspoons per day for 2 doses.
Children born with a large mass (4 kg or more), even under the condition that they are breastfed, have to be quite early, in the second month of life, as prescribed by a doctor, to enter into the daily diet fresh cottage cheesepounded with breast milk (1-2 teaspoons or more for 2-3 times).
From the age of four months, cottage cheese is given to all children, starting with one or two teaspoons and up to 20 g (four teaspoons), by the year - 40-50 g daily. Cottage cheese must be fresh, it must be obtained from the dairy kitchen, and if this is not possible, you should cook it yourself. Cottage cheese can be unleavened or sour, made from kefir or milk, fermented with kefir.
Recipes for cooking cottage cheese at home
Kefir is added to milk in the amount of 1/5 of the total volume and fermented in a warm place for 12 hours. For the preparation of cottage cheese kefir is heated over low heat. When the amount of whey reaches 1/3 of the total volume, the curd is reclined and cooled.
You can use a faster method of obtaining cheese from kefir. To prepare 50 g of cottage cheese, you need to take 200 ml of kefir, stir it, add 100 ml of chilled boiled milk, stir and put in a water bath (in a wider pan with water, the level of which should be above the mixture). When the milk is curled, the fire is turned off and the mixture is cooled to room temperature. Then it is filtered through the boiled gauze, squeezed, and the curd is ready. Kefir cottage cheese is tender, soft and better absorbed by the child's gastrointestinal tract.
You can cook cheese from fresh milk. To prepare 50 g of cottage cheese take 250 ml of milk and, heating it over low heat with stirring, pour a teaspoon of 10% calcium chloride into it, which is obtained in a pharmacy by prescription. Grains of coagulated protein will gradually appear in the milk. As soon as the milk boils, it is removed from the heat and allowed to stand. Cottage cheese is thrown back on a sieve, and then rubbed through it once. It should be remembered that when cooking cottage cheese at home it is extremely important to observe perfect hygienic conditions.
Egg yolk needed after three months of life. You need to start with 1/4 of the yolk and after 4-5 days increase to 1/2 of the yolk daily. The yolk should be cooked hard-boiled, thoroughly ground with breast milk, then it can be added to porridge or vegetable puree. Egg yolk is rich in salts of phosphorus, calcium, iron, vitamins A, D, B 1, B 2, PP, as well as high-quality protein and fat. In addition, egg yolk contains lecithin, which stimulates growth and development child's body, increases its resistance to diseases.