A newborn baby just born seems completely helpless. However, it is not. He possesses many of the skills inherent in nature, which are called reflexes.
Unfortunately, few parents are interested in how well such automatisms are manifested in their baby. Whereas, knowledge of the essence of each reflex reaction and methods of its testing will help to monitor the correctness of the child’s development, the state of his nervous system.
Unfortunately, it also happens that even pediatricians, to whom parents seek advice, cannot always boast the latest knowledge in the field of baby food. In such situations, you should always get acquainted with the results of recent scientific research, as well as analyze the recommendations of leading health organizations that will help you make the right decision.
A mother of two children tries to educate them in a spirit of intimacy and a sense of mutual trust. He works in Cheshire, UK, as a qualified volunteer to support other mothers with breastfeeding. An episode that is interesting and interesting for parents is when a newborn shows what psychology is called inborn reflexes. They are called so because they seem to be simple, uninvited responses to a particular stimulus. In short, a child just born already knows how to manifest itself in certain situations, even if you did not know about it or did not know about the actions in question.
What are reflexes
Reflexes are an automatic response of the organism to any stimuli. In the newborn period, which lasts a little less than a month (28 days), the baby has only unconditioned reflexes. With their help, the baby adapts to the outside world.
The presence of well-marked automatisms indicates a well-formed nervous system of the child. Therefore, in the first birthdays of the infant, the pediatrician and the neuropathologist will necessarily diagnose the degree of manifestation of all the necessary reflex reactions in him.
Psychologists believe that these newborn reflexes are not needed for long-term survival, although many of them will also help us to mature at the most critical moments. However, in the first part of their lives, they play the role of teachers in relation to the child, contributing to his neurological development.
What innate thoughts do babies have?
Newborn reflexes can be distinguished at the stages of satisfaction, when they are in the uterus of the mother and reflexively react to certain stimuli. At birth, the child has a set of 27 reflexes, each of which has a specific role. Among the most important and amusing for the viewer, we will mention the Moro reflex, the deep reflex, the passage reflex, the palm reflex, the swimming reflex and the reaction to the illusion of the abyss.
Many innate reflexes can be called up on a baby specifically by doing this in the form of gymnastics. The main thing is to make sure that the child is healthy and such exercises do not cause him any unpleasant feelings.
Reflexes of newborns are divided into two groups, depending on which part of the nervous system is responsible for their functioning:
- Motor segmental reflexes are provided by areas of the spinal cord and brain stem. They are divided into oral and spinal automatism;
- Posotonic supersegmental reflexes are regulated by the centers of the middle and medulla oblongata. These include automatisms that are responsible for controlling muscle tone, depending on the position of the head and torso.
Most of the unconditioned reflexes disappear over time. They are called rudimentary. The decay time of each reflex is different. Some automatisms are needed only at the adaptation stage, individual reflex reactions serve as the basis for new conscious skills and disappear as they are formed. There are some reflexes that remain in the child for life.
In turn, we will discuss each of these 27 newborn reflexes in order to better understand the behavior of the little ones. He is present in the behavior of the child up to 7 months, after which he disappears, for the most part. If he stays after 9 months, visit the family doctor, as this may be a sign of slowing down. You can monitor the Moreau reflector when you hold the support on which it lies on the head of the child. He will stretch his legs and legs, trying to "grab" the fall.
Bilateral absence of this reflex may indicate defects of the central nervous system, whereas unilateral absence of these reflexes may indicate birth defects, such as a fractured clavicle. In addition, some forms of paralysis may be suspected for some unilateral disappearances.
Types of reflexes
In total, there are 16 of the most significant reflex reactions of newborns.
Oral reflexes
First, consider oral reflexes. Their presence is very important for the baby, as they provide a sucking process.
- The sucking reflex is the ability of the newborn to make sucking movements. It manifests itself in any irritation of the oral cavity. It is worth the baby feel that in his mouth is an object, he tightly wraps it with his lips and tongue and begins to actively suck. Read more about \u003e\u003e\u003e
Sucking reflex fades very late. Supporters of self-radiation notice that the child forgets exactly how to suck the breast in the region of 3-5 years.
A deep or entrenched correction, as the specialists say, occurs as soon as the child is in the womb and disappears after the third or, at the latest, fourth month of life. Due to its deep diagnostic and adaptive value, this reflex is one that helps your baby to eat sucking. breast milk from the very first minutes of life.
You can follow the deep reflex if you touch the baby's cheek: he will turn his head to the touch, open his mouth and make movements, as if he was sucking from his mother. Passage reflexes occur in the first week of life in approximately 58% of newborns. Walking, an essential element in a person’s life, is known from the womb of the mother, but since the system of muscles and bones is not sufficiently developed in the first few months of life, it is forgotten to be taught.
- Swallowing reflex - provides the ability to swallow food that is in the mouth of an infant. This automatism persists throughout life;
- The proboscis reflex - is the ability of the baby to fold the sponge "tube". Such a reaction occurs after a quick touch or a light tap on the child’s upper lip. At the same time, he involuntarily shortens the round muscle of the mouth and the lips are pulled forward;
This reflex is necessary for making sucking movements. It disappears in 2 - 3 months after the birth of the baby.
You can observe the reflex of the passage when you hold the child in an upright position, with your feet on the stand. It can also be seen if you touch the sole of the child with your hand. Occurs after the fifth month of pregnancy in the fetus. 3 or 4 months after birth, he is independent and unconscious. After this age, it has been reorganized and included in voluntary seizure activities.
You can see the palm reflex, when - to the parents' disappointment - you put your finger on the child, and he pulls it up in his hand. Floating reflection also has diagnostic value. He disappears after 4 months. This is the ability of the child to remain on the surface and not to swallow water when immersed in it.
- The search or search reflex has this name because it is associated with the search for the infant's maternal breast. With a light touch of the corner of the mouth, the child turns his head toward the source of irritation, and his lower lip goes down.
When checking the searching reflex, you need to make very accurate touches. In addition to the corners of the mouth, you can press on the middle of the upper or lower lip. In this case, the child should accordingly tilt or tilt the head down. If it is wrong to do such manipulations as a result, you can get a demonstration of the proboscis reflex.
Try to observe the swimming reflex in the newborn only in specially organized centers and under the close supervision of qualified personnel. It is dangerous to experience this at home, because the child’s muscles are not sufficiently developed, and he gets tired very quickly and can cause accidents.
An early reaction to the illusion of the abyss causes much controversy among psychologists, not knowing whether it is innate or acquired after birth as a result of the action of factors. I am sure that a child aged 2 or 3 months will experience a change in heart rate when he is put on a translucent base plate.
- Babkin's reflex is the following process: when pressing on the palms of the newborn (in the area of the tubercle from thumb) he opens his mouth and bends his head in search of his chest. By 2-3 months this reflex reaction should disappear.
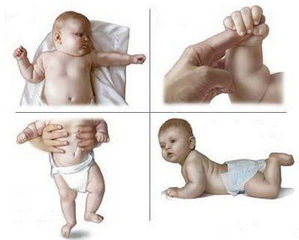 Spinal automatisms are equally important for a newborn. These include all other types of involuntary movements of the child, which he makes the body and limbs.
Spinal automatisms are equally important for a newborn. These include all other types of involuntary movements of the child, which he makes the body and limbs.
That is why a child, even older, will refuse to yield himself on the bed, even to encourage his mother, regardless of whether he approached her. A tonic or reflex "fencer" is one that entertains the audience in particular. This is bending the arms and legs towards the head of the child.
This is the answer to the gadilat. A reflection of surprise occurs when a child is suddenly afraid of something. He throws his head back, loosening the arms and legs. The reflection of crying is the first communication tool used by children. The auditory reflex is often used by doctors to test a child’s hearing ability. When you strike the child’s ear with your fingers, it turns its head in the direction from which noise is heard. If the child does not respond to this stimulus, consult your family doctor.
- The grasping or monkey reflex is the unconscious squeezing and holding in the palms of an object. Usually, to test such automatism, adults place their baby’s index fingers in the palm of their hands. However, he firmly captures them and does not let go.
The child must hold so tightly that it can thus be raised above the surface on which he lies. By the age of 3–4 months in a baby, this reflex is replaced by deliberate actions when it stretches and picks up an object on its own.
A flashing reflection occurs when something goes to the child’s face to protect the eyes by closing the eyelids. If the child does not show this reflex, consult your family doctor. The paper recipe appears when a child is exposed to strong light. He will turn his head or keep his body.
The reflex reflex is also necessary for survival. Immediately after a deep reflex through which saliva occurs, the child will swallow. The painful reflex can be tested by gently holding the newborn on the soles of the foot. He will almost immediately pull out his leg. If your child does not respond to this stimulus, consult your family doctor.
- Protective reflex - is the ability of the newborn when putting it on his stomach to immediately turn his head to the side. This automatism allows the infant to breathe in any position of his body. Over time, the child learns to lift and hold the head, and this reflex reaction will disappear. See also: \u003e\u003e\u003e
- Plantar reflex - triggered by pressing a finger on the sole in the area of the second and third fingers. In this case, the newborn must preload the toes. Thus, the tonic response of the flexor of the toes is checked.
- Babinski's reflex - is also checked on the foot of the infant. To do this, you need to make a stroking movement on the outer edge of the foot in the direction from the heel to the fingers. Reflexively, the fingers are stretched and spread out to the sides (fanlike).
- Reflex support and straightening - is the ability of the baby to rest on the surface with a full foot. To test this automatism, the child needs to be suspended, fixing its head, and then lowering it down. In the raised position, the baby’s legs are tucked into the abdomen, but when the surface touches, it leans on it and straightens the body. Such automatism persists for quite a long time, up to 8 - 11 months.
- Automatic walking reflex - checked simultaneously with the previous one. After the child has stood up and straightened, he is slightly bent forward. The baby must make several walking movements on the surface. Sometimes in the process of such walking his legs can cross. After a month and a half, the baby must learn to rearrange the legs correctly. Learn consciously \u003e\u003e\u003e.
- Crawling reflex - manifests itself if you put a newborn on the belly. He begins to make chaotic movements of the body, trying to budge. At this time, you need to substitute the palm to the soles of the baby. In response to such irritation, his movements should be activated. At 4 months, the child ceases to show a similar reaction. Now he will try to build on the support and move forward. Read more about \u003e\u003e\u003e
- Reflex Moreau - it can be described as a "reaction to fear." To check, you need to put the newborn on the changing table and with two hands simultaneously hit the table on both sides near his head. First, the baby must sharply spread his arms to the sides, open his fingers, straighten his legs, but then quickly return to the starting position.
- Reflex Galant - allows you to check the reaction of the spine to the stimulus. It is necessary to lay the baby on its side and from top to bottom to run his fingers on both sides of the paravertebral lines. At the same time, he will arch his back.
Pozotonichesky reflexes
Pozotonic reflex reactions are associated with the formation of the child's ability to raise the head, sit or stand, which implies the ability to properly redistribute the load on the muscles depending on the position of the body.
A trembling reflector occurs when the body needs more oxygen. This happens, especially when he is tired, because organ systems can no longer supplement oxygen demand. Babkin's reflection occurs when you lightly press the palm of your child. He will open his mouth and bend his arms, trying to suck.
The reflex head reflex can be noticed when you put your child in a funnel without supporting his head. He will try to keep him straight, but he will not get a good result, because he does not yet have a muscular system for development. Reflex walk can be seen when you put the baby on your stomach. He will raise his head a little and try to crawl forward. This is useful for preventing choking a child.
- The Magnus-Klein reflex is also called asymmetric cervical tonic automatism. Pre-newborn need to put on his back and turn his head on its side. The arm and leg on the side where the child will be turned will straighten, and on the opposite side will bend. This position is called the "fencer pose."
Such a reflex reaction dies away when the infant reaches the age of two months.
Cross-reflex extension of the lower limbs - this is what causes the child to move his foot over the other, if you touch his foot with his finger. When you are lying on your stomach, touch the baby on one side of the column. If he does not bend with the part to which he touched, perhaps there may be a disease.
In this case, consult your family doctor. The orientation reflection can be seen by touching the “four shining points” of the face, namely the forehead, the area under the lips and each of the two cheeks. The child must move his head or body in each of these areas. He disappears after the 9th month of life.
- Symmetric tonic cervical reflex - is the actuation of the flexors and extensors of the extremities when the head tilts and tilts. When throwing back - the child straightens his arms and bends his legs, and vice versa.
These reflexes are observed in infants constantly.
Violations of reflex reactions
Verification of reflexes is a mandatory procedure for diagnosing the correctness of a child’s development. In the event of any deviations in the manifestation of reflexes in the newborn, it is necessary to undergo an urgent consultation with a specialist. Timely correction allows the infant's body to quickly recover and further develop without pathologies.
Rottalian reflexes are one of the constant reflexes that can be observed throughout their lives. Its deficiency indicates engine problems in the age of adults. The naso-palpebral reflex can be seen by percussion of the nasal root, with the child's eyes open. He must close them immediately.
The reflection of the doll's eyes occurs when the head slowly turns to one side. Your child’s vision will remain fixed. Respiratory reflexes, of course, are important for survival and appear from the very first moments of birth, consisting of breathing and breathing.
So what do you need to pay attention to?
First of all, it is important to remember that a newborn should manifest absolutely all of the listed reflex reactions. Premature babies, as well as babies who had asphyxia or birth trauma at birth, unconditioned reflexes expressed more faintly.
Be sure to follow the periods of extinction of rudimentary automatisms. If after the expiry of the designated periods the reflex reaction remains pronounced, this indicates a violation of the activity of the central nervous system.
When a child stops responding to stimuli
Reflection of protection occurs when the child feels the need to defend himself in front of the situation, turning his head or raising his hand. All of these 27 reflexes are tested by doctors who participated in the birth of their child or pediatrician. Their disadvantage may be a signal of a malfunction in the neurological system of the child, for example, a delay or some malfunction of the motor system.
If you notice a lack of an inborn reflex in your child in the first few months of life, consult your family doctor and ask for advice. However, you do not need to worry: your child may have passed the reflex stage, or you have not applied the correct test. Do not start worrying until you speak with a medical specialist, and only after you have a good idea.
Also an unfavorable indicator is abrupt change (strengthening or weakening) reflexes in the newborn. This may be due to:
- muscle tone disorders, more on this: \u003e\u003e\u003e;
- pathology of the nervous system;
- inflammatory diseases;
- drug reactions.
When checking the manifestations of reflexes should consider such points:
- A slight increase in the reflex reactions of the infant may be observed with increased nervous excitability;
- Oral reflexes are most pronounced in the period before feeding. When a child is full, he may not manifest them so clearly;
- The reflex response to the stimulus must be the same on both sides.
Of course, it is important to pay attention to the general condition of the infant. If, with changes in the manifestation of a reflex reaction, there are no other neurological pathologies, then this may be an individual feature of the organism of the newborn and will not adversely affect its further development.
The main thing is that the doctor, after the examination, concluded that “the physiological reflex reactions of the infant are normal”. Such a diagnosis means that your child feels good and is healthy with his health.
The involuntary tonic movement of a paralyzed limb in response to a certain irritation of its skin is called a protective reflex. Protective reflexes in most patients are found on the lower limbs with a lesion of the spinal cord in its thoracic region and are often more flexural in nature.
Reflex flexion type is expressed by involuntary flexion of the limb in the ankle, knee and hip joints, leading to the "shortening" of the limb. The extensor reflex, on the contrary, causes “lengthening” of the limb due to its involuntary straightening in the hip, knee joints and plantar flexion of the foot. Of course, such a protective reflex can be obtained with a bent limb. Protective reflexes are often accompanied by pain in the affected limb. Most often, these reflexes cause, irritating the skin with a stroke motion of a needle, prick, pinch, touching it with something cold. In this case, the stimulus must act for quite a long time. A protective reflex can also be obtained in response to a passive movement in a joint. For example, with a sharp passive flexion of the toes of the foot, dorsal flexion of the limb in the knee and hip joints occurs (Bechterew's protective reflex).
With brain damage, protective reflexes are observed especially often in the initial period, gradually weakening further. The latter are less characteristic of residual hemiplegia, with the exception of the lower extremities, where they can be observed for a long time and in the late hemiplegia phase. Protective reflexes are pronounced (poor prognosis) in the early stages of extensive brain shutdowns (fresh extensive hemorrhages or thrombosis, hemorrhages of the ventricles of the brain, encephalitis, extensive head injuries, etc.), appearing mostly during a comatose state. In such cases, they are expressed in hemiplegic type, mainly on the upper limb; the induction of protective reflexes can contribute to the development of spontaneous tonic convulsions of the protective type, which, merging with each other, sometimes lead to significant hypertension (the so-called early contracture).
NK Bogolepov indicates that in necrotic processes in the brainstem or in the region of subcortical nuclei, the protective reflexes of the upper limbs are more often extensor, while in the foci in the cortex and underlying white matter they are more flexural. If the patient survives in the acute period, the reverse development of protective reflexes occurs quickly. Protective reflexes were first described by J. Wabinski in 1898.